Are IoT products and services as customisable as they say they are?
Website Editor • September 2, 2019
The Internet of Things is transforming every corner of life: the home, the office, city streets and beyond.

The Internet of Things is transforming every corner of life: the home, the office, city streets and beyond. IoT products give us greater control over door locks, lights and appliances; resource consumption habits; business processes; and better connect us to the people, systems and environments that shape our daily lives.
What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the millions of physical devices around the world that are now connected to the internet, collecting and sharing data.
Because of cheap processors and wireless networks, it's possible to turn anything, from a pill to an aeroplane, into part of the IoT. This adds a level of digital intelligence to devices, enabling them to communicate without a human being involved, and merging the digital and physical worlds.
A lightbulb that can be switched on using a smartphone app is an IoT device, as is a motion sensor or a smart thermostat in your office or a connected streetlight. An IoT device could be as fluffy as a child's toy or as serious as a driverless truck, or as complicated as a jet engine that's filled with thousands of sensors collecting and transmitting data back to make sure it is operating efficiently. At an even bigger scale, smart city projects are filling entire regions with sensors to help us understand and control the environment.
IoT and consumers
IoT promises to make our environment - our homes and offices and vehicles - smarter, more measurable, and chattier. Smart speakers like Amazon's Echo and Google Home make it easier to play music, set timers, or get information. Home security systems make it easier to monitor what's going on inside and outside, or to see and talk to visitors. Meanwhile, smart thermostats can help us heat our homes before we arrive back, and smart lightbulbs can make it look like we're home when we're out.
IoT and businesses
Occasionally known as the Industrial IoT, the benefits of the IoT for business depend on the implementation. Enterprise use of IoT can be divided into two segments: industry-specific offerings like sensors in a generating plant or real-time location devices for healthcare; and IoT devices that can be used in all industries, like smart air conditioning or security systems.
IoT security and privacy?
Security is one the biggest issues with the IoT. These sensors are collecting in many cases extremely sensitive data - what you say and do in your own home, for example.
Researchers found 100,000 webcams that could be hacked with ease, while some internet-connected smartwatches for children have been found to contain security vulnerabilities that allow hackers to track the wearer's location, eavesdrop on conversations, or even communicate with the user.
IoT evolution: Where does the Internet of Things go next?
As the price of sensors and communications continue to drop, it becomes cost-effective to add more devices to the IoT. As the number of connected devices continues to rise, our living and working environments will become filled with smart products -- assuming we are willing to accept the security and privacy trade-offs.
The IoT has a lot to offer not only for consumers but for businesses as well. Today's companies need to take full advantage of IoT devices, platforms and tools to build business models that will thrive in a more connected world.
At Adapt Ideations
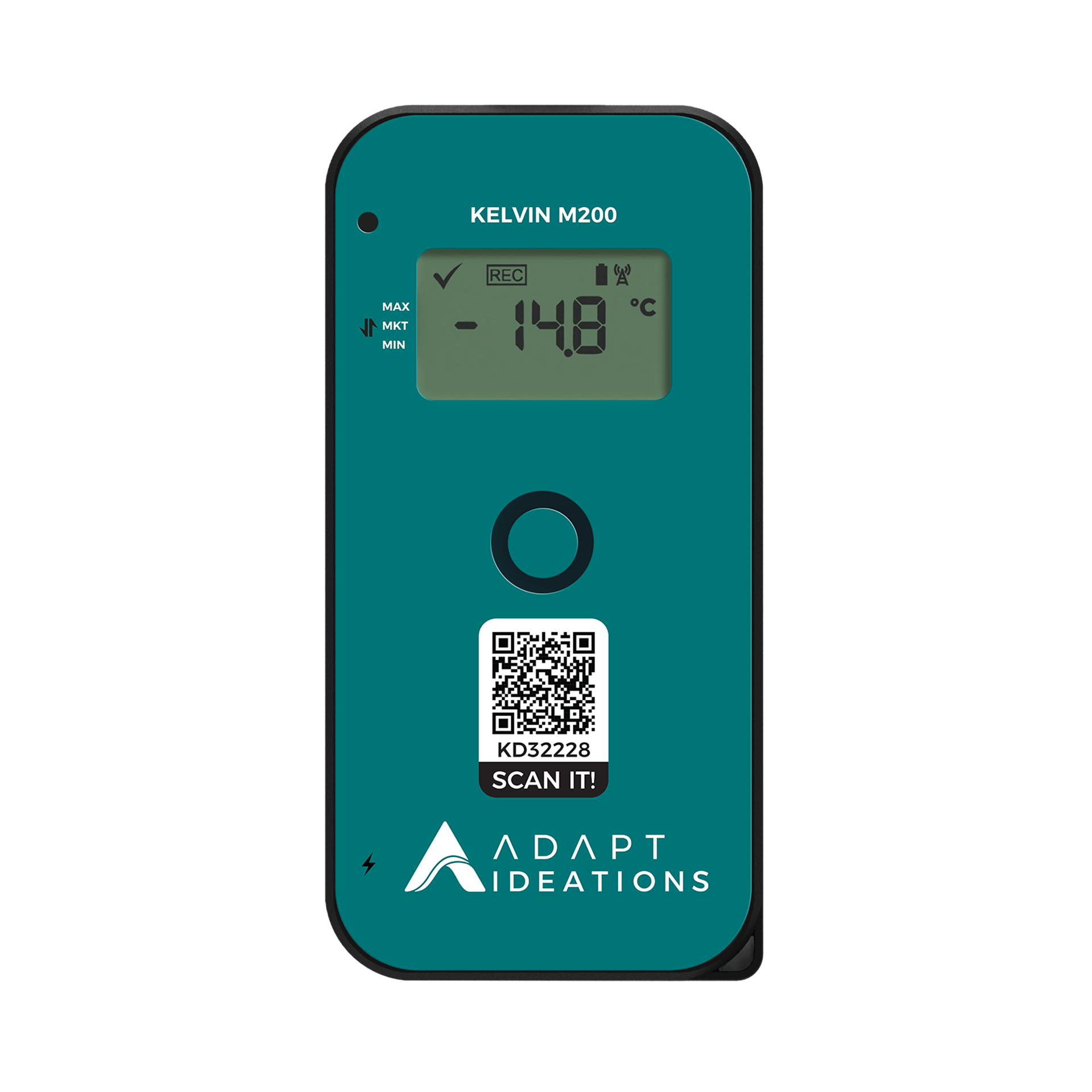
we’ve tested and innovated the most popular options the IoT has to offer, from smart vehicle surveillance solutions
to temperature sensitive consignment tracking solutions. At Adapt Ideations we pride ourselves in our innovative customisable one-stop solutions.
Are you ready to take your company to the next level?
Share Our Post.
Awards & Recognition

Best Temperature Monitoring Solution Provider
Awarded by India Biologics & Vaccines Outstanding Industry Awards 2022

Adapt Ideations Recognised As A Supply Chain Leader
by Alcott Global on Supplify's Supply Chain Tech Map 2.0

Related Articles.
The global landscape of healthcare is evolving rapidly, with vaccines playing a pivotal role in preventing and mitigating diseases. The World Health Organization (WHO) underscores the critical need for vaccines to be stored and transported at specific temperatures to ensure their efficacy and safety. The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the fragility of global vaccine distribution, emphasizing the importance of maintaining the cold chain during transportation and storage. Importance of Cold Chain in Vaccine Distribution The efficacy of vaccines is intricately linked to the maintenance of the cold chain. The global cold chain packaging market is projected to grow at a substantial CAGR of 14.8% from 2023 to 2033, driven by the escalating demand for temperature-controlled packaging solutions, especially in the pharmaceutical industry. This growth is indicative of the increasing recognition of the significance of the cold chain in preserving the efficacy of vaccines. The Role of Active Track & Trace Solutions Amid the challenges posed by maintaining the cold chain, the emergence of the active track and trace solutions has become a game-changer in ensuring the integrity of vaccines. 1. Real-Time Monitoring for Vaccine Integrity Active track and trace solutions provide real-time monitoring, offering a dynamic and immediate response to deviations from the recommended conditions. This capability is instrumental in preventing temperature excursions that could compromise the quality of vaccines during transportation and storage. 2. Automated Alerts for Swift Intervention One of the key benefits of active track and trace solutions is their ability to generate automated alerts. In the event of any deviations from the optimal temperature and other vital conditions, stakeholders receive instant notifications. This swift intervention minimizes the risk of vaccine wastage and ensures that corrective measures are taken promptly. 3. Data Analytics Enhancing Decision-Making Beyond real-time monitoring and alerts, active track and trace solutions contribute to data analytics. The integration of analytics provides valuable insights into the performance of the cold chain. Decision makers can leverage this data to optimize supply chain processes, further enhancing the efficiency of vaccine distribution systems. Challenges in Vaccine Tracking The pharmaceutical industry faces unique challenges in tracking and distributing vaccines, especially in the wake of global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. 1. Increased Demand and Market Growth The global vaccine market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.74% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by the escalating demand for vaccines worldwide. The Asia-Pacific region, with its rapidly growing market, is at the forefront of this expansion. The surge in demand poses challenges in efficiently meeting the needs of diverse populations. 2. Vaccine Distribution Challenges The COVID-19 pandemic had triggered a surge in demand for vaccines globally, highlighting the need for efficient and effective distribution systems. Advanced technologies, including active track and trace solutions, play a pivotal role in overcoming the challenges posed by increased demand and ensuring a seamless distribution process. The Intersection of Technology and Vaccine Distribution To overcome the challenges of vaccine tracking and distribution, the pharmaceutical industry is increasingly turning to advanced technologies. 1. Blockchain and AI for Enhanced Efficiency and Security The utilization of technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence (AI) holds great promise in improving the efficiency and security of vaccine distribution systems. Blockchain, with its tamper-proof ledger, enhances supply chain security. AI, on the other hand, analyzes vast datasets, providing insights that can be utilized to optimize supply chain operations. 2. Global Cold Chain Logistics Market Growth The global cold chain logistics market is projected to grow at a significant CAGR of 15.1% from 2021 to 2028, emphasizing the increasing demand for temperature-controlled logistics solutions. This growth further underscores the need for advanced technologies to ensure the integrity of temperature-sensitive products, with active track and trace solutions at the forefront. Maersk's Perspective on Cold Chain Logistics Maersk's whitepaper on the state of cold chain logistics provides insights into the pressing need for advanced technology adoption in the global supply chain. 1. Technology Enhancement Goals With 75% of the global supply chain seeking more technological enhancements by 2026, the demand for IoT solutions, including active track and trace solutions, is becoming more critical. Maersk emphasizes the need for a technological revolution to address the challenges posed by the increasing complexity of the global supply chain. 2. Roadblocks: Personnel and Change Management While the benefits of IoT technology are evident, roadblocks such as personnel and change management hinder the full-scale adoption of these technologies. Overcoming these challenges requires a strategic approach to training and organizational change, ensuring seamless integration into existing supply chain processes. Digital Transformation in Pharma Supply Chain The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the need for a more resilient and agile supply chain. 1. Supply Chain Challenges and Opportunities The pharmaceutical industry faces numerous challenges in optimizing its supply chain processes. These challenges include counterfeit drugs, lack of visibility, product recalls, supply chain disruptions, complex inventory management, data security, and stakeholder collaboration. However, amidst these challenges lie numerous opportunities for improvement through digital transformation. 2. Opportunities Unveiled by Digital Transformation Digital transformation offers the pharmaceutical sector multiple opportunities to enhance its supply chain. Technologies such as IoT, blockchain, and AI can revolutionize the industry. a. Enhanced Visibility Through IoT Digital technologies such as IoT provide real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, enabling greater transparency and accountability. This is particularly crucial in ensuring the integrity of temperature-sensitive products like vaccines. b. Reduced Lead Times and Improved Quality Control By automating and streamlining repetitive processes, digital technologies can significantly reduce lead times, resulting in faster product delivery and increased customer satisfaction. AI and machine learning can enhance quality control by analyzing large datasets, identifying patterns, and enabling proactive quality management. c. Cost Savings and Sustainability Digital transformation can result in significant cost savings for pharmaceutical companies by reducing waste, improving inventory management, and optimizing processes. This is crucial for ensuring the profitability and sustainability of the industry.

Overview After experiencing multiple lockdowns and restrictions globally during the pandemic Adapt Ideations saw a clear answer to overcoming challenges such as manufacturing delays or orders requiring a quick turnaround. This led the company to identify regional manufacturing support that could be utilized to meet these necessary requirements. Adapt Ideations turned to Circuitwise , a local Australian manufacturing company to diversify our manufacturing. Problem A significant takeaway from the global pandemic highlighted the need for regional manufacturing support due to prior reliance on international manufacturers. Not only were periodic delays experienced, but turnaround times between product testing and challenges with global logistics to our regional hubs were felt throughout the pandemic. This led Adapt Ideations to seek regional manufacturing support in order to combat future challenges experienced from solely relying on overseas based suppliers for manufacturing our products. Regional support can also be utilized for smaller orders or when a quick turnaround is essential for orders placed. In most cases our clients have a significant number of devices in circulation at any point of time. An important aspect of the devices in circulation is managing them effectively particularly over a number of different sites. In order to achieve this, Adapt Ideations provides customers the ability to use mass charging boards in which a number of devices can be charged at the same time without individually having to connect each device to a USB cable and subsequently into a power socket to charge. Solution In a company first, Adapt Ideations partnered with Circuitwise , a local Australian manufacturing company to meet the requirements of an order for mass chargers that needed to be fast tracked. With Adapt Ideations largely working with clients who handle cold chain products that are often highly regulated, partnering with a supplier who maintains a high level of reliability & safety standards and has demonstrated experience working with similar industries is paramount to ensure consistent high standards are maintained. The benefits of partnering with a regional manufacturing supplier can be measured on a number of metrics such as experiencing a quicker turnaround to better meet the needs of our clients when required, eliminating the need for globally importing products and cost savings associated with smaller orders placed. Future After the first successful project working alongside Circuitwise, Adapt Ideations hopes to expand the partnership and work with Circuitwise on a number of future projects. Their commitment to high quality standards and collaborative approach has been fundamental in supporting us throughout our first project with Circuitwise. “Increasing supply chain resilience post pandemic has been a significant focus area for Adapt Ideations. Our collaboration with Circuitwise provides a strategic assurance to our ANZ supply network while supporting the drive to promote manufacturing in Australia. We look forward to more exciting projects in the coming days.” - Anirban Gupta Co-Founder and Director, Adapt Ideations Circuitwise CEO Serena Ross said she was pleased to see another company realize the benefits of manufacturing in Australia, particularly for small to medium-sized production runs. “There are many good reasons for manufacturing in Australia ,” Serena said, “including speed and reliability, responsiveness, ease of communication, reduced tariffs and intellectual property protection.”

Temperature-controlled logistics is a crucial aspect of global supply chains, particularly in the pharmaceutical industry. Maintaining the correct temperature during transportation is not just a logistical issue but also a critical factor in ensuring the safety and efficacy of life-saving vaccines and other temperature-sensitive products. As the demand for temperature-sensitive products like vaccines and biologics continues to surge, ensuring their safe transportation is paramount. Any deviation in temperature during transit can compromise the efficacy of these products, leading to significant financial losses and potential health risks. This blog delves into the evolution of temperature-controlled logistics, critical challenges faced in this sector, and groundbreaking innovations that address these challenges. With a focus on real-time monitoring through IoT solutions, we aim to showcase the advancements that contribute to the efficiency and compliance of global pharmaceutical supply chains. Evolution of Temperature-Controlled Logistics Temperature control has undergone a remarkable transformation in the last two decades. Stringent global regulations, customer demand for new temperature ranges, emerging markets with extreme temperatures, and the growing value of drugs like biologics have been essential driving forces. These factors have spurred the evolution of temperature-controlled logistics to meet the demands of a rapidly changing world. The landscape of temperature-controlled logistics is evolving, thanks to technological advancements. Trends include the growing availability of prequalified shippers simplifying the validation process, sophisticated supply chain services, a rising interest in reusable packaging, and advances in temperature-monitoring technology. These innovations contribute to the industry's ability to adapt and thrive in a dynamic environment. Temperature-controlled logistics involves managing the flow of products through a cold chain. Divided into food and pharmaceutical sectors, the global market size of cold chain logistics is projected to grow significantly. From USD 242.39 billion in 2021 to USD 647.47 billion by 2028, exhibiting a CAGR of 15.1%, the industry is expanding rapidly, reflecting its critical role in modern commerce. 3 Key Challenges in Temperature-Controlled Logistics Compliance Issues Stringent Regulatory Standards: Global temperature-controlled logistics operates within a framework of strict regulations set by health and safety authorities. Meeting diverse regulatory requirements across international borders poses a significant challenge for companies in this sector. Documentation & Reporting: Compliance involves meticulous documentation and reporting of temperature-sensitive shipments. Keeping up with the evolving documentation standards requires streamlined processes and robust systems. Validation & Qualification: Ensuring the validation and qualification of equipment and processes according to regulatory standards is an ongoing challenge. The need for continuous validation adds complexity and time constraints to logistics operations. Risks of Temperature Deviations Product Integrity: Temperature-sensitive products, especially pharmaceuticals and biologics, are highly susceptible to temperature deviations. Even brief exposure to temperature breaches during transit can compromise the integrity and efficacy of these products. Financial Implications: Temperature deviations can lead to significant financial losses for companies. Replacing or disposing of compromised products and potential legal repercussions contribute to financial challenges. Supply Chain Disruptions: Temperature deviations can disrupt the entire supply chain, leading to delays in product availability. This not only affects businesses but can have critical implications for healthcare providers and patients relying on timely access to medications. Security & Theft Concerns Value of Cargo: Temperature-sensitive cargo, such as pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and high-value perishable goods, can become a target for theft. The significant value of these products heightens security concerns throughout the supply chain. Vulnerability During Transit: The vulnerability of cargo during transit, particularly in unsecured areas, poses a constant risk. The potential for theft during transportation adds complexity to securing temperature-controlled shipments. Need for Tracking & Monitoring: Ensuring the security of temperature-sensitive cargo requires robust tracking and monitoring systems. Integrating security features, such as real-time location tracking and tamper-evident technologies, is essential to mitigate theft risks. In navigating the intricate landscape of temperature-controlled logistics, companies must address these multifaceted challenges to uphold compliance, safeguard product integrity, and ensure the security of valuable shipments. Innovative solutions, such as advanced monitoring technologies and comprehensive security measures, are crucial in overcoming these challenges and fostering a resilient and efficient supply chain.